-
Welcome to SEFP!
Foundation Design For A Ware House (Steel Structure)
-
Recently Browsing 0 members
- No registered users viewing this page.
-
Our picks
-
Performance Based Seismic Design
Howard Roark posted a topic in General Discussion,
Hi there,
I am interested in performing "Performance Based Design" for a 20 story building.
I'll be performing "Non-Linear Static Pushover Analysis" for my model. Until now, I have decided to go with "Displacement Co-efficient method". I will be using ETABS 2017 for performing Pushover Analysis. While assigning plastic hinges, I have an option of using ASCE 41-17 (Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Existing buildings". I would like to know what would be a better estimate for relative distances for plastic hinges in case of beams, columns. Any input concerning assignment of hinges to beams, columns and shear walls is highly appreciated. Normally it's taken 0.05 and 0.95 or 0.1 and 0.9. What's your opinion on this?
Secondly, it would be great if someone can recommend me a book or some good source to understand how to characterize building using performance levels. Any sort of help is appreciated.
I have recently graduated and joined a structural design firm, so kindly guide me, considering me a beginner.
- 2 replies
-
Beam Column Joint
Badar (BAZ) posted a topic in Journal/ Articles/ Tutorials,
*SEFP Consistent Design*<br style="background-color:#ffffff; color:#272a34; font-size:14px; text-align:start">*Pile Design*<br style="background-color:#ffffff; color:#272a34; font-size:14px; text-align:start">*Doc No: 10-00-CD-0007*<br style="background-color:#ffffff; color:#272a34; font-size:14px; text-align:start">*Date: April 16, 2018*
1.1. FUNCTION OF JOINT
Beam-column joint must transfer the forces, such as moment, shear and torsion, transferred by the beam to the column so that the structure can maintain its integrity to carry loads for which it is designed.
Another function of the beam-column joint is to help the structure to dissipate seismic forces so that it can behave in a ductile manner.
1.2.WHY DO WE CARE
During an extreme seismic event, the code-based structure is expected to maintain its load-carrying capacity for gravity loads even after the structure deforms into inelastic range so that it does not pose any life safety hazard. Hence, the joint can go through significant degradation of strength and stiffness, and if it fails in shear, or anchorage, the life-safety objective of code cannot be achieved.
1.3.CONSEQUENCES OF FAILURE
1.4.THINGS TO CONSIDER FOR BEAM COLUMN JOINT
Longitudinal bars of beams, or slab, must be able to develop their yield stress, so that the beam/slab can transfer moment to joint. It means that longitudinal bars must have adequate development length for hooked bars. This implies that the size of the column must be such that bars can develop their tensile forces. If bars can transfer moment, they can also transfer shear as far as monolithic construction is concerned.
The shear strength of the joint must enable the transfer of moment and shear through it.
The joint should be Constructible: Congestion of reinforcement is the main concern.
1.5.DESIGN SHEAR FOR BEAM COLUMN JOINT
The design shear for beam-column joint depends upon the relative strength of beam and column at the joint.
- 4 replies
-
Comments/Observations regarding modelling in ETABS
Badar (BAZ) posted a topic in Journal/ Articles/ Tutorials,
*Comments/Observations regarding modelling in ETABS*
*Doc No: 10-00-CD-0006*
*Date: May 06, 2017*
Some of the observations made during extraction of results from ETABS (v 9.7.4), for design of reinforced concrete members, are being share in this article.,
1) Minimum Eccentricity
ETABS always considers the minimum eccentricity for selecting the design moment of columns irrespective of the probable behavior of the column, whether short or long column. See section 10.10.6.5 and its commentary of ACI 318-08 which deals with minimum eccentricity of long columns. You should always check the design moments that ETABS uses for columns if you want to bring down the cost of construction.
2) Unbraced/ Braced Preference
ETABS always performs analysis of frame as if it is un-braced. You should investigate if the storey under consideration is braced, or un-braced (10.10.5.2), and decide appropriate design moments of columns.
3) Time Period
ETABS has a tendency to select a time period of the building that is considerably less than the value obtained by the approximate method, Method A, of the section 1630.2.2 of UBC 97. To quote the FEMA 451 document: ''Because this formula is based on lower bound regression analysis of measured building response in California, it will generally result in periods that are lower (hence, more conservative for use in predicting base shear) than those computed from a more rigorous mathematical model". So, there is no need to use the value of time period that is lot less than Ta. One should always check the time period used by the software; ETABS can overestimate the seismic force by more than 2 times.
Visit the forum link to read the complete article.
Link: http://www.sepakistan.com/topic/2300-commentsobservations-regarding-modelling-in-etabs/- 0 replies
-
Minimum Reinfocement Criteria For Crack Control
abdulqadeer29 posted a topic in Concrete Design,
The minimum amount and spacing of reinforcement to be used in structural floors, roof slabs, and walls for control of temperature and shrinkage cracking is given in ACI 318 or in ACI 350R. The minimum-reinforcement percentage, which is between 0.18 and 0.20%, does not normally control cracks to within generally acceptable design limits. To control cracks to a more acceptable level, the percentage requirement needs to exceed about 0.60% (REFRENCE ACI COMMITE REPORT 224R-01)
So according to above statement , should we follow 0.60%, to be on more safe side??
- 12 replies
-
First South Asia Conference on Earthquake Engineering (Karachi)
Fatima Khalid posted a topic in General Discussion,
Dear Sir/Madam,
This email is an invitation for the participation in the First South Asia Conference on Earthquake Engineering (SACEE-2019) which will be held on 21-22 February 2019 in Karachi, Pakistan. This conference is the inaugural event in this series of conferences which has been constituted under the auspices of South Asia Earthquake Network (SHAKE). The organisers of the conference include NED University, University of Porto, University of Fuzhou, University Roma Tre and Institution of Engineers Pakistan. The conference website can be visited at http://sacee.neduet.edu.pk/.
Please note that world leading earthquake engineering experts have confirmed their participation in the conference. These include Prof Abdelkrim Aoudia (Italy), Prof Alper Ilki (Turkey), Dr Amod Mani Dixit (Nepal), Prof Bruno Briseghella (Italy), Prof George Mylonakis (UK), Prof Khalid Mosalam (USA), Prof Humberto Varum (Portugal) and many others. The presence of these distinguished experts allows you to exchange your work/issues with them and discuss possibility of any future collaboration. Please note that participation in the conference is strictly based on registration. Early registration in different categories at reduced rates are available till 10 December 2018. Please visit the conference website to see the details and the link for registration.
If there are any queries, please do not hesitate to contact the Conference Secretary at the following address
Prof. Muhammad Masood Rafi
Conference Secretary- SACEE-2019
Chairman
Department of Earthquake Engineering
NED University of Engineering & Technology Karachi, Pakistan.
Phone: 0092-21-992-261261 Ext:2605
Email: rafi-m@neduet.edu.pk- 1 reply
-
Minimum reinforcement For Precast Pile
Dr Yueh posted a topic in Foundation Design,
What is the Minimum reinforcement For Precast Pile according to different codes (ACI,BS)?? Pile length is 40 times of pile least dimension .-
- 1 reply
-
-
ETABS model for factory building
Palash Engr posted a topic in Concrete Design,
Dear members, I am working on a 10 storied rcc factory building with one basement, where floor loads are in general 125 psf(Live) . but there are 2 warehouse in the building at ground floor & 10th floor where the Live load of stacked materials are 450psf. I have modeled it and analysed in ETABS. After analysis, seeing the floor displacement for seismic load, i am in big shock to see the pattern. the displacement pattern suddenly increased hugely & then got normal . if the warehouse load created problem, then why it effected only Ground floor level, not the 10th floor! Please tell me how can i solve it.-
- 1 reply
-
-
Underground water tank base slab as a foundation
Fatima Khalid posted a topic in Foundation Design,
Asalamualaikum all,
I have columns which are conflicting with the underground water tank as shown in figure.
So I have decided to make underground water tank base slab as a footing for column. So I import etabs model to safe and just take uniform water load on base slab and point load from columns.
This is the residential house. The BC is 2tsf. But SAFE is showing tension on the base slab and the thickness from punching is 30''. I believe that thickness is too high. What can be the error? Is this approach is correct for design base slab of ugwt to carry load of two edge columns?-
- 11 replies
-
-
Safe Iterative Uplift Analysis
asadishaq posted a topic in Software Issues,
SAFE perform iterative uplift analysis,any one having experience how to check the results of this analysis???what is the purpose and scope of this analysis???- 15 replies
-
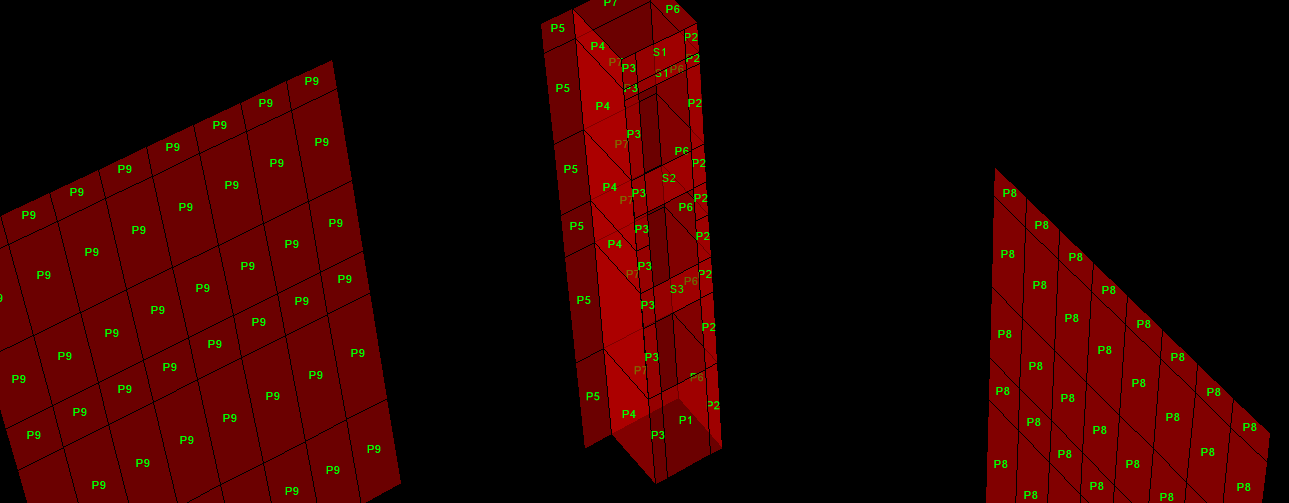
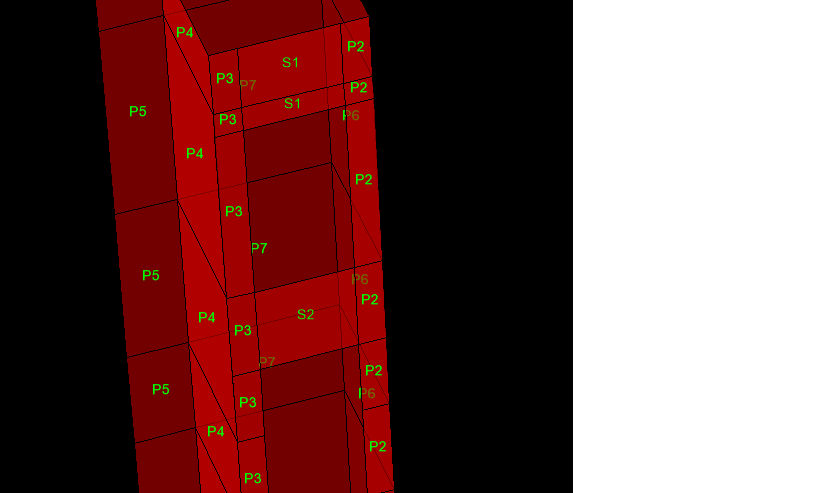
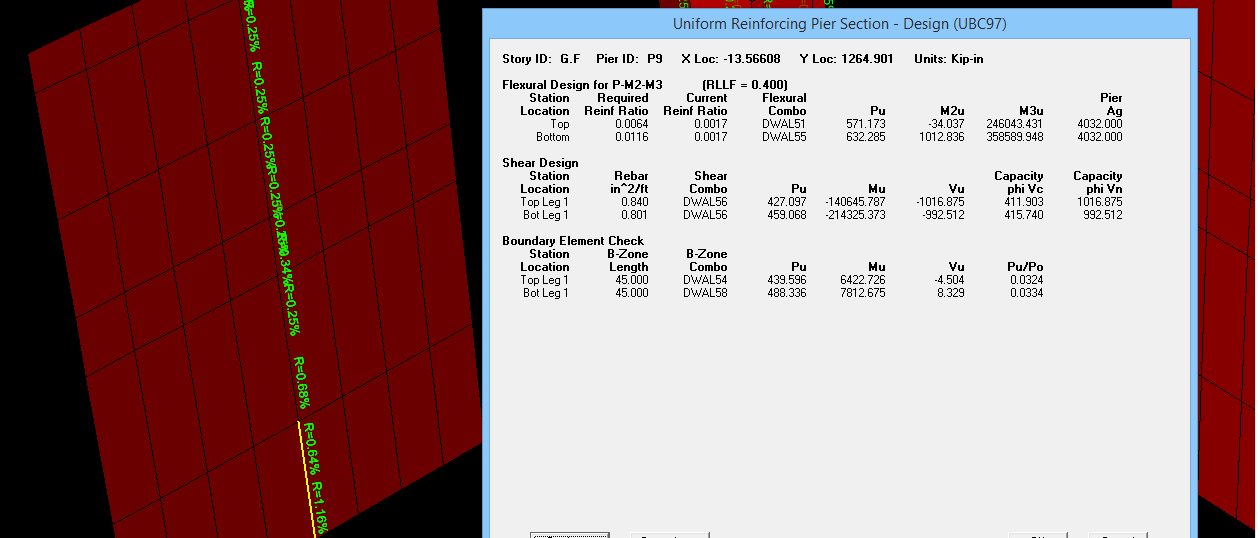
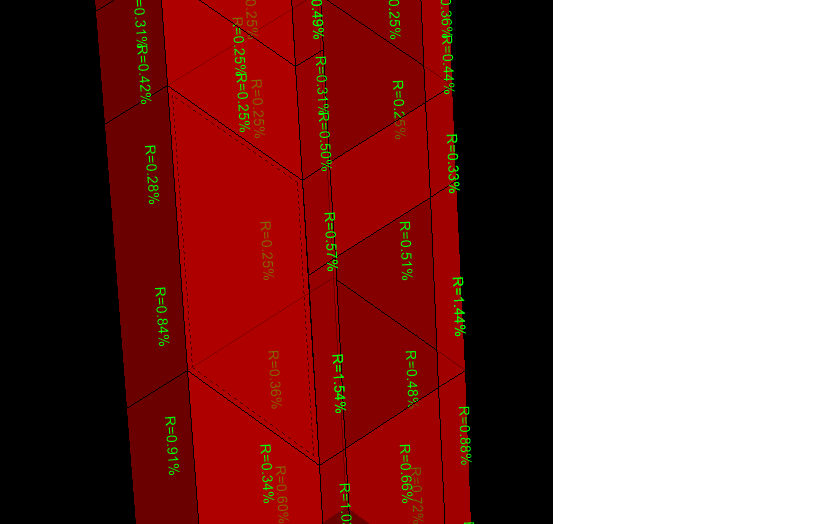
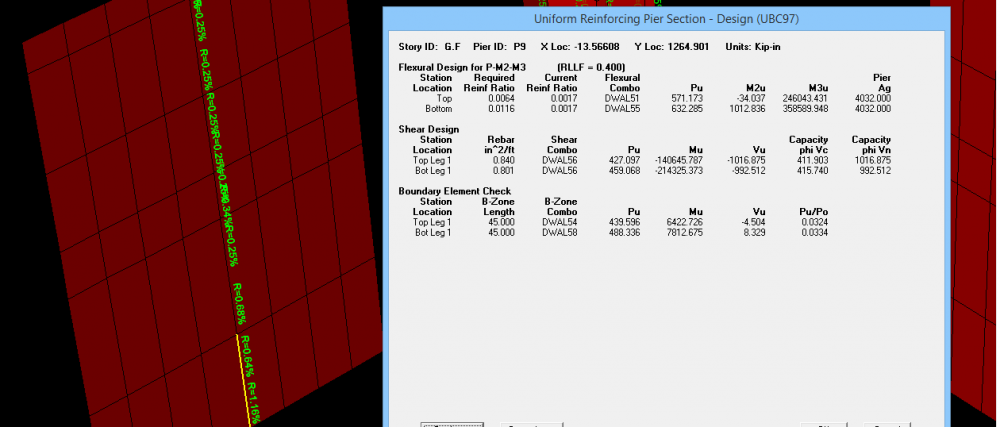
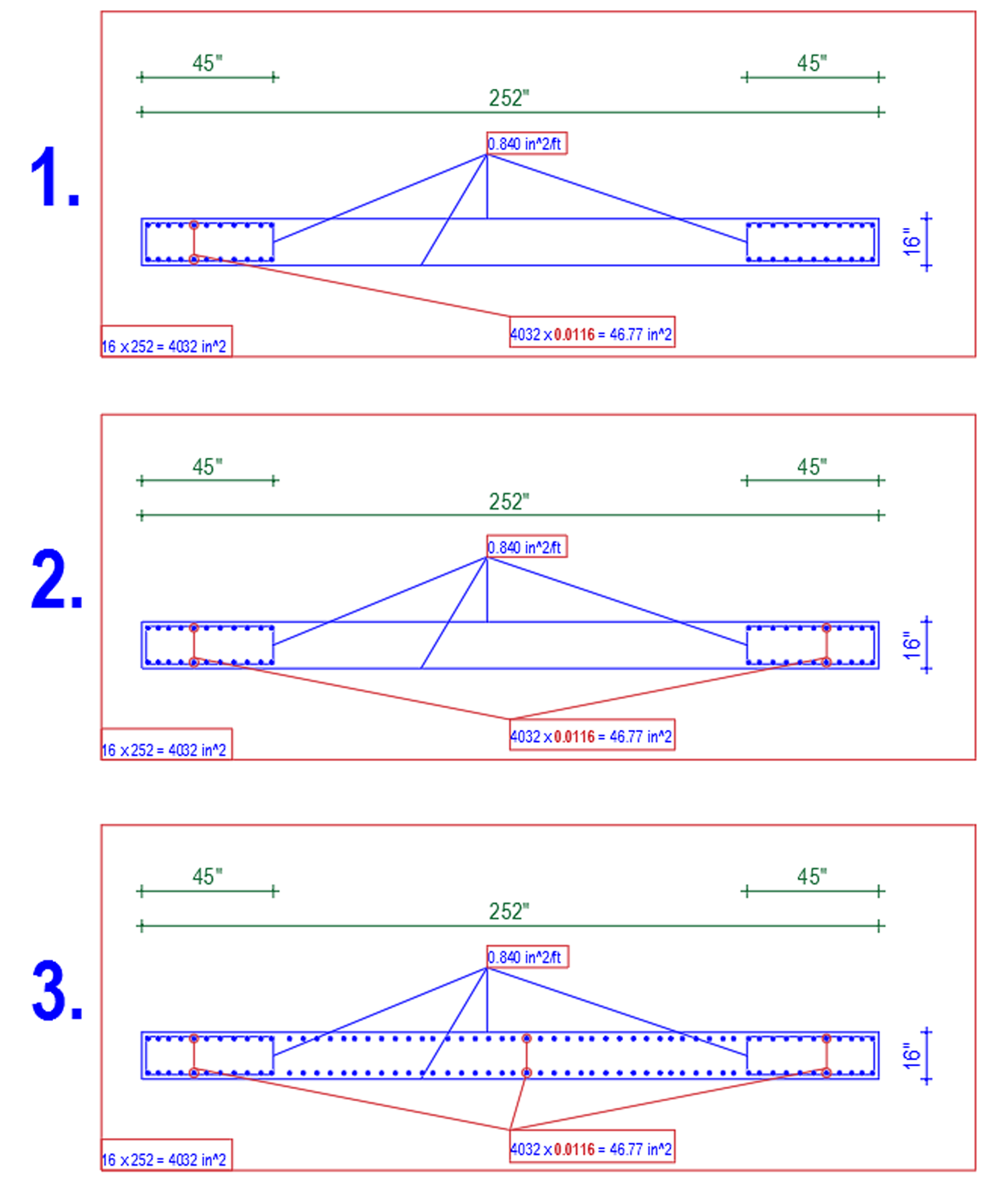
Shear wall design
farooqbro posted a topic in Concrete Design,
AOA
i am facing problems in shear wall design .what are the pier and spandral ?what will be the difference when we assign pier or spandral? without assigning these the shear wall design is incomplete .
i am taking about etabsv16
someone have document about shear wall design plz provide it
thank you
- 13 replies
-
-
Tell a friend








Recommended Posts
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now